The most active metals are the elements of groups I and II, located on the left side of the periodic table. A metal is considered active when it reacts strongly and quickly with other elements. The reactivity of a metal increases as we move from the top to the bottom of the periodic table.
The exception is hydrogen, which is not considered a metal and is located in the upper left corner of Mendeleev's periodic table of chemical elements.
The most active metals in the world
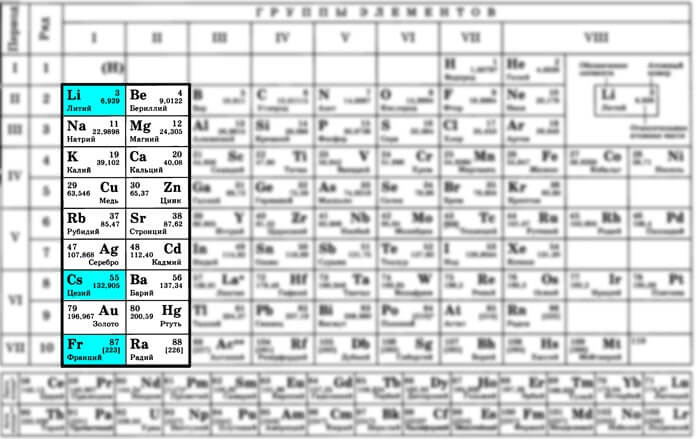 According to the reactivity of the metal elements listed in the periodic table of chemical elements, they are divided into three groups:
According to the reactivity of the metal elements listed in the periodic table of chemical elements, they are divided into three groups:
- Active metals.
- Metals of medium activity.
- Low-active metals.
The most active metals on Earth are lithium, cesium and francium.
Cesium is the most active of the non-radioactive elements. It is a rare silver-yellow shiny metal with an atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) of 55. It is a very soft element that will melt in your hands - if it does not explode sooner, as it reacts strongly to moisture.

There is also a highly radioactive element, francium, which may be more active than cesium. Or it may not, we will probably never know, because francium is not only extremely radioactive, but also extremely rare.
The last of the three most active metals - lithium - has an interesting property. It gives a crimson color to the flames.
Here is a video demonstration of the activity of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium and cesium.
What is cesium
Cesium belongs to alkali metals. They are highly reactive and do not occur freely in nature. These metals are also very ductile and are good thermal and electrical conductors.
Cesium was the first element that could be detected with a spectroscope. In 1860, it was discovered by German chemists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff when they analyzed the spectrum of mineral water from the Bad Dürkheim spring.
Cesium occurs naturally in the minerals pollucite and lepidolite. It is also found in many aluminosilicates such as beryl, petalite and carnallite. The richest known cesium deposit is located in Canada, on the shores of Lake Bernick Lake. About 70% of all earth's reserves are concentrated there. Curiously, this lake is the site of the annual Cesium Festival (February 24), when tons of this substance are burned in the snow, and another cesium frenzy prevails.
Cesium is also a byproduct of nuclear fission in reactors.
Cesium properties
 Let cesium and not the heaviest metal in the world, but it is the most active and has a number of unique properties:
Let cesium and not the heaviest metal in the world, but it is the most active and has a number of unique properties:
- It burns spontaneously in air and instantly explodes on contact with water or moisture in any form, even with ice down to -116 C.
- It burns with a brilliant blue flame. To the uninitiated, the flame appears purple rather than blue, but after enough meditation, studying works of chemistry, and blissful hours spent in awe of cesium burning, the true blue nature of its flame is revealed.
- The name "cesium" comes from two bright blue lines in its emission spectrum. Translated from Latin, "caesius" means "sky blue".
- Its hydroxide (liquid molten state) is capable of eating through flesh, glass and many other substances. Only the metal rhodium and a number of its alloys are able to withstand the melt of cesium hydroxide.
- Cesium iodide and bromide are used as central components in the manufacture of high-precision optics, including scopes, goggles and night vision binoculars. Cesium has also been used experimentally in ion propulsion systems for spacecraft due to its low ionization potential.
- Cesium is used to create the most accurate atomic clocks. Even the best wristwatch in the world may be a few seconds or even a minute behind. But atomic clocks based on cesium only lose one second in five billion years.
- Natural cesium consists of one stable isotope, Cs 133. There are 30 other radioactive isotopes known to fill the range from Cs 114 to Cs 145. Cesium-137 (aka radiocesium) is one of the most biologically hazardous components of radioactive waste and nuclear fallout. It accumulates in living organisms and even in fungi, and its highest content is found in reindeer and waterfowl in North America.
Humans and animals are constantly exposed to minimal amounts of cesium by eating, breathing, and drinking. Although it is unlikely that we will get sick from cesium alone, long-term exposure can lead to adverse health effects, including nausea, vomiting, bleeding, and cell damage.
Cesium and cancer treatment
Even Paracelsus argued that everything is poison, and everything is a medicine. It's just the dosage. And when it comes to cesium, the words of Paracelsus are absolutely correct.
Cesium is currently being investigated for the treatment of several forms of cancer, including brain tumors. Cesium-131, a radioactive isotope of cesium, is placed along with another radioactive isotope (iodine-125) in a brachytherapy capsule ("seed").
According to the American Brachytherapy Society, a brachytherapy capsule is a radioactive "pod" that is placed directly into cancerous tissue. These seeds are effective for several forms of cancer, including prostate, cervical and endometrial cancers.
In one study, a group of 24 patients with brain tumors were implanted with cesium-131 brachiotherapy seeds in the tumor. There were minimal side effects, but patients generally tolerated this form of treatment well.
The idea of using cesium-131 brachytherapy seeds as a cancer treatment dates back to the 1960s and was described in a study published in the journal Radiology. A 2009 study published in the journal Medical Physics discussed the use of cesium-131 seeds to treat prostate cancer with positive results.
More research is needed before cesium treatment can take its place in medicine. So far, however, studies have shown that the use of cesium-131 to treat cancerous tumors with brachiotherapy is encouraging.
Comparison of cesium and france

Like cesium, francium (Fr) belongs to alkali metals (only radioactive) and has extremely high chemical activity.
- The density of france is 1.87 grams per cubic centimeter, which is comparable to the density of cesium - 1.879 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Cesium and francium are two of the four metals that become liquid at room temperature. Mercury and gallium have the same property.
- The interaction of cesium with water occurs very effectively - with an explosion, the formation of hydroxide CsOH and hydrogen H2. Francium and water also do not particularly "love" each other, and when they interact, the strongest alkali is formed - francium hydroxide.
- Like cesium, francium accumulates in living organisms.Therefore, the isotopes of this metal have found their application in medicine, for the diagnosis of cancer and various biological research.
- But in terms of prevalence, cesium is far ahead of francium. About 20 tons of concentrated cesium ore are mined in the world every year. According to PeriodicTable, cesium is the 50th most abundant element in the earth's crust. France, in the entire earth's crust, has about 340 grams.
That is, the properties of the two most active metals on the planet are very similar.
Comparisons of cesium and lithium

Lithium is one of the top 3 most active metals on the planet. It is a key component in the batteries that power smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. More than half of the world's lithium supplies come from the "lithium triangle" - Bolivia, Chile and Argentina. The largest source of lithium from salt is the Chilean Atacama Desert.
- Like cesium, lithium is an alkali metal. And, like cesium, it occurs in nature only in the form of compounds. Moreover, traces of lithium are found in almost all igneous rocks and in many mineral springs. It was one of three elements created by the Big Bang, along with hydrogen and helium.
- There is little lithium and cesium in the earth's crust - 21 g / t and 3.7 g / t, respectively.
- If cesium ignites in air, interacting with oxygen, then lithium can even be stored in the open air for some time. Due to this "tolerance", lithium is the only alkali metal that does not require storage in kerosene. It can also convey “fiery greetings” when interacting with oxygen, but only at high temperatures.
- Lithium is the least dense metal (0.533 g / cm3). Cesium has a much higher density - 1.879 grams per cubic centimeter. The lightness of lithium means that it can store energy without adding gravity to various devices.
- But in terms of low melting point, lithium gives a head start to cesium. Its melting point is 180.5 degrees Celsius. And cesium melts already at 28.4 degrees Celsius.
- But lithium boils quickly - at 134 degrees, but it is not easy to bring cesium to a boil, a temperature of 678 degrees is required.
- Both lithium and cesium are easily cut with an ordinary knife.

